What is a VPN? A VPN, or “Virtual Private Network” is a technology that creates an encrypted, private connection on a public network so that data can be sent and received with an extra layer of security.
But how does a VPN work and why should you worry about personally using one? If you’re concerned about your online privacy and security, this is an important question to answer.
Be sure to subscribe to the All Things Secured YouTube channel!
It is estimated that there are close to 4.57 billion people accessing the internet globally each month. That number continues to climb at a crazy rate.
Like it or not, the internet is here to stay.
With this increase in global internet literacy, it seems logical that online security would be a top priority for users…and yet this doesn’t always seem to be the case.
As you can see in this insightful online security infographic, even though more than 50% of consumers recognize a need for a VPN, less than 30% actually use one .
Strangely, the highest adoption rate comes from the unlikely countries. You can see the comparison between VPN usage in the USA and UK and other countries.
Our ignorance of VPNs portrays our lack of understanding about internet security. Downloading an antivirus or just using a good password manager app and hoping for the best is the common approach to internet security.
In this article, we’re going to cover the following topics.
Understanding what a VPN is, how to use one and even which are the best personal VPNs is becoming more important with each passing day.
Note: Some of the links in this article may be affiliate links, which means that at no extra cost to you, I may be compensated if you choose to use one of the services listed. I only recommend what I personally have used, and I appreciate your support!
What is a VPN or “Virtual Private Network”

Let’s begin by giving a simple answer to the question “What is a VPN?”, one that even non-tech savvy people can understand.
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a secured, personal express lane on the internet highway. Instead of having your internet activity travel on public roads like everybody else, a VPN connects you to your destination via your own personal tunnel (encryption) that nobody else can use or see, giving you a more secure and private experience.
Now I’ve already explained this earlier, but let’s start here with what the letters “VPN” stand for.
- V – Virtual
- P – Private
- N – Network
When we access the internet on our phone, tablet or computer, we are entering a massive public network that connects the entire world.
As confusing as this sounds, you can think of the internet like the highway system that connects different cities across the country. You travel with hundreds of other vehicles on public roads and they can see exactly where you’re going.

But what if you had the ability to drive your own private tunnel instead of the highway.
You’d probably take that, wouldn’t you?
I know I would. And that’s exactly what a VPN does for you.
On the internet highway, a VPN creates a dedicated lane that is encrypted so that nobody else can see what you’re doing, where you’re going or where you’re coming from.
Although it can be used for a number of different purposes (bypassing censorship, privacy, security over public networks, etc.), the main function of a VPN is encryption.
The VPN server is like your identical twin in another location. Connecting to a server in another country makes it seem as if your location is in that other country.
How Does a VPN Work?
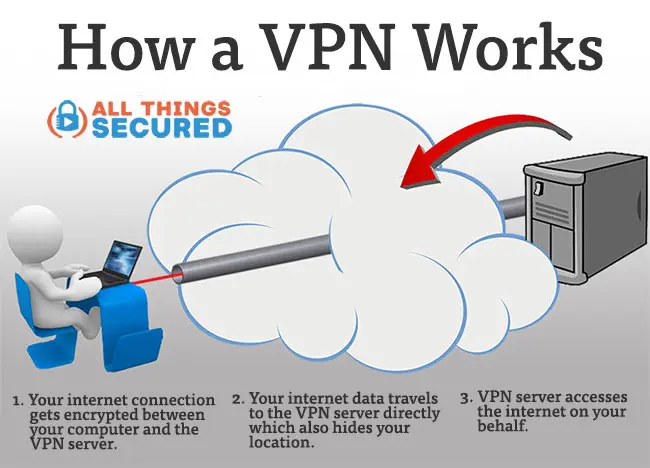
A virtual private network operates by giving you encrypted access to a computer server operated by the VPN provider. As mentioned above, this connection allows you to browse the internet in “stealth mode” by building a secure tunnel between you and the internet.
If you want another analogy, you can think of the internet as a cloud. The secure tunnel is the secure connection between you and the remote server.
When you first download and open a VPN client (a software that helps you connect to a server), you’ll have the option to choose from one of hundreds/thousands of servers.
These servers are located all across the globe, as you can see in this example from the NordVPN software.
When a selection is made, the encrypted tunnel is created between your location and the location of the server. There are a number of ways to build this tunnel, known as “VPN connection protocols”. Some of these protocols offer greater security while others offer more speed (more on this below).
When connected to the server, you are now accessing the internet from the location of the server, not your physical location.
Benefits of Encryption & Location Masking
Perhaps you understand the analogy of the internet like a highway system or a cloud, but you still don’t understand why you would need one.
Don’t worry, you’re not alone.
Thankfully, the benefits are easier to understand than you might imagine. Let’s look at a few of the most important benefits:
- Internet Privacy: When you connect to the internet, especially on a public network (i.e. airport or coffee shop WiFi), there is a risk when transmitting your internet data. While using https websites already encrypts your data, using a VPN adds an extra layer of protection and a safety net in case you access an http website by accident.
- Location Spoofing: The ability to access the internet from what appears to be a different location is particularly useful for content that is geo-blocked or geo-restricted. Let’s say you’re traveling to Asia for a trip but you still want to watch your favorite movies or TV shows. In this case, a virtual private network will allow you to stream Netflix in a country like China where all access is blocked.
- Anonymity: Did you know that when you connect to the internet, your computer is assigned a number (known as an IP address) that provides a lot of information about your location? Using a VPN hides this IP address, thus providing you with more anonymity as you surf the internet.
Maybe you won’t be traveling internationally and you don’t care if somebody knows the location of your computer.
However, in this age of government spying and identity theft, if you ever find yourself connecting to a public network…
…a VPN is an extremely important consideration.
Why aren’t more people using a VPN?
At this point, you must be wondering why everyone isn’t using a VPN. The use of a Virtual Private Network isn’t as ubiquitous as it should be because:
- It slows down your internet speed. It takes a lot of processing power to encrypt and reroute internet traffic. This is especially true if you’re using higher encryption. The additional route your data has to travel through another server also results in reduced speeds. The greater the distance between your location and the location of the virtual private network server, the slower the speed.
- Good personal VPNs cost money. While there are a limited few free VPNs that I recommend, most I tell people to avoid. Most of the free options either have several ads or sell your information. Some may even practice both. Additionally, these free services only hide your IP address. They don’t protect your privacy. It is, therefore, better to subscribe to a premium service, which will charge a nominal fee of $2-$5/mo. Nevertheless, the cost is still a deterrent for some people.
If you’re experiencing reduced internet speeds, you’ll want to read through these 5 steps you can take to increase speeds while using a VPN.
Understanding VPN Connection Protocols
The tunnel created between your device and the virtual private network server is built using what is known as a “connection protocol”.
If you need more details, read more about these connection protocols here. Each protocol has its own strengths and weaknesses and not every software gives you the option to choose how you connect.
The bottom line is this: Whether you realize it or not, you have to use a connection protocol to connect to a server. So what options are there to choose from?
Most Common VPN Connection Protocols
Although there are a number of protocols available, we’re going to cover five of the most common connection protocols, and one newer protocol:
- OpenVPN: This is the most secure connection protocol and therefore the most recommended if you have a choice. One reason for this is that it is the only open source VPN connection protocol.
- PPTP: This stands for “point-to-point tunneling protocol”. It is a faster connection but also not quite as secure as OpenVPN.
- L2TP/IPSec: which stand for “Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol” and “IP Security” respectively. It’s considered slightly more secure than PPTP but slower than OpenVPN.
- SSTP: This stands for “Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol”. This protocol was developed for the Windows operating system, so it mostly only works on Windows computers.
- IKEv2: This stands for “Internet Key Exchange version 2”. Works best on mobile devices and is considered highly secure.
OpenVPN is the industry standard and most secure commercial software. In most cases, your provider will default to an OpenVPN connection.
However, there is a newer security protocol called WireGuard that is quickly becoming even more popular than OpenVPN. It’s fast, lightweight and considered to be even more secure than all the older options.
There are some companies like Mozilla that only offer WireGuard as a connection option and a growing number of VPNs that offer Wireguard. In most commercial services, though, you’ll probably have a choice between a few different connection protocols.
Brief History of Virtual Private Networks

The history of the Virtual Private Network dates back to 1996 when Gurdeep Singh-Pall invented the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP).
His invention was motivated by the desire to find a way for people to work remotely on company tasks over a secure internet connection (can you imagine a world before remote work?!).
In its early days, a virtual private network was exclusively used by corporations primarily for remote working purposes.
Virtual Private Networks have been around for a long time and are widely used.
Although this security feature hasits roots in the corporate world, it has now become more popular among personal users. As hacking and identity theft become common, the usage of encryption software has risen.
Are VPNs Legal to Use?
One final question that most people tend to ask is whether or not they are legal to use.
A virtual private network can be used for privacy and security, but it can also be used to hide illegal activity. Understanding this is key to answering this question of legality.
A VPN itself is not illegal…but it is often used for illegal activity.
In most countries, we are given the right to basic privacy. This includes a right to use a tool like a virtual private network, as long as we aren’t doing illegal activities (copyright infringement, unethical hacking, etc.).
There are some countries, however, where this is a bit of a grey area. These countries include China, Iraq, and many others in the Middle East.
The simple answer is that yes, it is legal to use . However, there is a more nuanced answer to the legality of VPNs that you can read as well.
How to Install a VPN on Your Device
Thankfully, installing the software on your computer, tablet or phone isn’t as daunting as you might first think.
Sure, there are manual ways to set up a VPN that are difficult to understand, but there are also automatic ways that even a 5th grader could do. I’ve developed a number of helpful tutorials to guide you through the process.
We’re going to cover the two most common places you’ll be installing this software: on your computer and on your phone.
Installing a VPN on Your Computer
To set up a virtual private network on your computer, you’ll want to follow the steps outlined in this video published on the All Things Secured YouTube channel.
As you can see, the process is fairly seamless and takes less than 15 minutes if you’re using a premium service such as the ExpressVPN example.
How to Install a VPN on an iPhone iOS
Installing a virtual private network on an iPhone is also the same as installing on your iPad. And honestly, since we’re talking about apps here, it’s practically the same for Android as well.
There are three primary ways that you can set it up on your iPhone:
- Manually
- via an App
- via your Internet Browser
Watch this video for an example of each.
In this video, I use the NordVPN app as an example, but the setup process will feel familiar no matter which you decide to use.
Final Thoughts | Securing Your Internet
A VPN is important for your internet security, especially if you travel frequently and use public Wi-Fi. It also allows you to avoid government censorship and utilize online services that are restricted to particular geographical locations.
For recommendations, check out our list of the best VPNs on the market today.
Great strides have been made towards creating highly secure VPNs that provide you with a private and secure internet connection. A server connection that uses an OpenVPN, charges a monthly subscription fee, and guarantees your internet privacy and security is one worth exploring.
You don’t need to be a great computer master in order to access and effectively use the security software.
Stop making excuses. Find a secure VPN provider today.







If I wanted to use a streaming service like Netflix for example, would I have to install a different version of Netflix
No, you wouldn’t Cliff. You might have to restart the app after you connect to the VPN, but Netflix immediately starts treating you like you’re in the country where you connect to the VPN server.
I don’t use my computer outside of my house. I do banking and shopping online. I also do a few things online with my cell phone. Do I still need a VPN and does it help block things when I’m using the internet on my cell phone?
These are good questions, Gloria. Honestly, in your case, you likely don’t need a VPN unless you’re using public WiFi a lot with your cell phone, but even then it’s more of a backup security than actively blocking things.
No, it won’t. The reason is because you have the ability to turn a VPN on or off. While you’re on public WiFi, you turn it on. When you’re on your home network, you turn it off. It’s that simple! 🙂
What are your thoughts on IPVanish?
You can read my review of IPVanish here if you want to get my thoughts 🙂
CAn i make use of a vpn when trading FOREX to spoof my location to another country in order to bypass certain trade restrictions in the eu?
Hmm…it’s possible, but I would double check that what you’re asking doesn’t break any laws that could get you in trouble.